Uh oh, is your phone or laptop battery starting to bubble up like a fresh can of soda? That hissing and swelling sensation is never a good sign. Battery bubbling can indicate dangerous gases building up inside, threatening to leak or even explode. But before you panic, take a deep breath and assess the situation calmly. Though it may look alarming, some gentle bubbling is normal, especially in older batteries. The key is knowing when it’s gone too far. With the proper precautions, you can take control before things get messy. In this article, we’ll cover what causes battery bubbling, how to tell if yours is still safe, and what to do when it’s time to say goodbye to your bulging battery.
Recap in Brief
Seeing your battery bubble and swell while charging is concerning, but don’t panic. Gentle bubbling can be expected in older batteries. However, excessive bubbling indicates dangerous internal pressure buildup, and you should stop charging immediately. If the battery feels very hot, emits any odors, or you see leaking, dispose of it immediately. Swollen batteries pose fire and injury risks. For mild bubbling, stop charging, let the battery cool down completely, then check if it’s still functional. If it’s expanded but works, continue using it cautiously until replacement. Inspect regularly for new bubbling, heat, or odors for safe usage. Discard immediately if issues persist.

Causes of Battery Bubbling
Lithium-ion batteries power most of our modern devices, from phones to e-cigarettes. Though energy-dense, they contain reactive chemicals prone to gassing when operating outside normal conditions. Thankfully, knowing the root causes can help you prevent battery bubbling issues.
Overcharging
The number one cause of battery bloating is overcharging. Excess electrical current drives damaging chemical reactions when you continually charge a lithium battery past total capacity. This generates gas bubbles inside the battery, leading to swelling. Both excessive voltage and amperage levels during charging can lead to overcharging and gassing.
High Voltage
High voltages beyond the battery’s specifications will also cause internal gas formation. Phone batteries are designed for around 3.7 volts of charge. Higher voltages can force electrons into the battery too vigorously, creating gas bubbles and swelling. Avoid cheap generic chargers with incorrect voltages.
Sulfation
As batteries discharge, sulfur crystals naturally form on the anode. When batteries sit unused for long periods, excessive sulfur buildup (sulfation) occurs. The sulfur inhibits current flow, damaging cells. Gas pockets form as a result. If unused, prevent sulfation by charging batteries at least once every 2-3 months.
Internal Short Circuits
Short circuits within a battery’s cells can generate intense localized heat, gas production, and swelling. Shorts are often caused by physical battery damage from impacts or manufacturing defects. There is no fix for a shorted battery aside from replacement.
Faulty Charging Systems
Defective, damaged, or improperly calibrated charging systems can overload a battery during charging. This leads to gassing and swelling. Always use the manufacturer’s official charger designed for your device’s battery chemistry and capacity. Avoid knockoff chargers.
In summary, lithium-ion batteries can bubble up like freshly poured soda when overcharged, exposed to high voltages, damaged internally, or charged with a faulty system. With care, you can avoid the blotches of battery bloat.
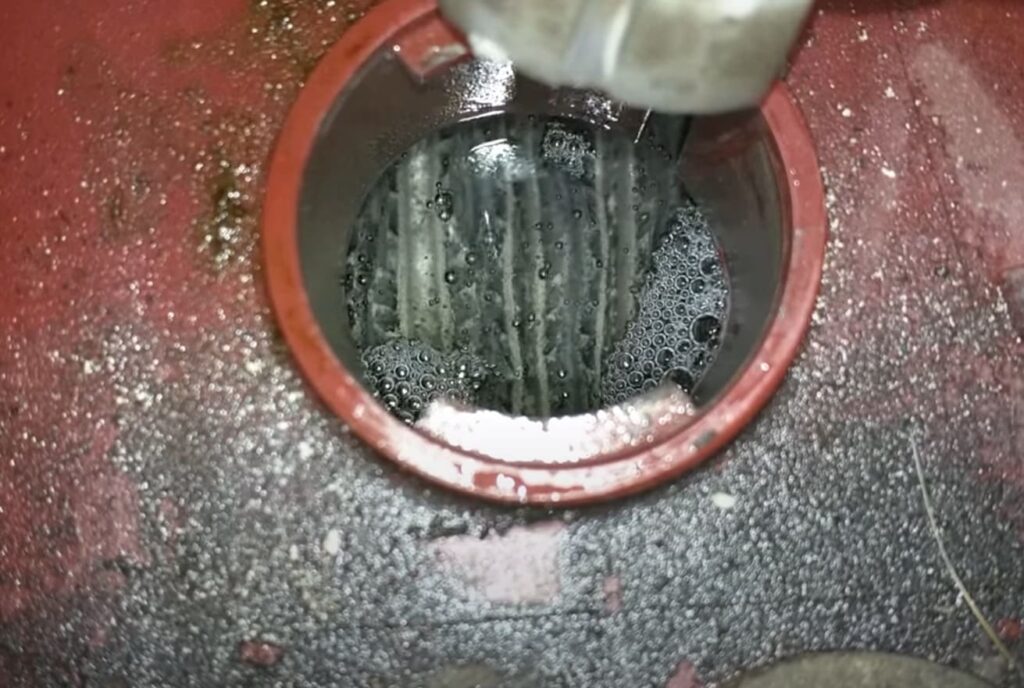

Effects of Battery Bubbling
Lithium-ion battery bloating is caused by gas buildup inside the battery’s cells. This internal pressure distorts the battery casing outward. But the swelling is merely a symptom of a potentially hazardous situation.
Damage to the Battery
The gas pockets forming inside a bloated battery cause irreversible damage to its structure. The swelling stretches the aluminum pouch material beyond its elastic limits. The pressure also deforms the battery layers and current collectors.
Swelling cracks electrode coatings, inherently reducing battery capacity and lifespan. The corrosion caused by electrolyte decomposition further degrades performance. These combined effects mean a bloated battery will need replacement sooner rather than later.
Safety Issues
The greatest danger with a puffed battery is the threat of fire or leakage. As swelling progresses, the electrolyte fluid can be forced out through ruptures in the battery seals. Leaked battery fluid contains caustic and flammable substances.
Gas pressure buildup also increases the risk of an internal short circuit. This can prompt thermal runaway, where the battery generates enough heat to combust. Swollen batteries are especially prone to shorting when punctured or crushed.
Bulging batteries become unstable and may explode violently if charged further or overheated. While rare, such battery fragmentation can cause severe lacerations and burns.
To mitigate hazards, swollen batteries exhibiting leakage, heat, or deformity should be identified and adequately disposed of immediately. Never attempt charging or operating a bloated lithium-ion battery. Replace it to restore your device to working order with power safety.
In summary, the effects of battery bubbling include reduced battery lifespan and performance, electrolyte leakage dangers, increased short circuit and fire risk, and the potential for explosive failure. Address swelling issues promptly before your battery becomes a liability.

What to Do When Your Battery is Bubbling
Battery bubbling is caused by gas buildup and points to declining battery health. Though unnerving, a systematic response can mitigate any safety issues. Here is an action plan for responding to battery swelling.
Stop Charging Immediately
First, stop charging the battery immediately if you notice swelling during the process, and continue to assess bubbles for the problem. The battery is being overcharged if bloating occurs.
Inspect the Charging System
Check your charger, cable, and charging port for damage after stopping the charge, as these could be overcharging the battery and causing gassing. If anything is damaged, stop using it until it is replaced. Use only manufacturer-approved charging accessories to avoid issues.
Wear Eye Protection
Before handling a swollen battery, wear protective eyewear in case of leakage. Caustic battery fluid in the eyes can cause permanent blindness. Play it safe when dealing with damaged batteries.
Unplug the Charger
Once protective eyewear is on, unplug the charger from the wall. This ensures no accidental reconnection occurs. Do not try removing cables from an actively charging swollen battery.
Disconnect Battery Clamps
Finally, after the charger is unplugged, remove the charging clamps from the battery terminals. Wait 15 seconds after opening to avoid dangerous sparks. Now, the battery is fully isolated and safer to transport for disposal.
In summary, swollen batteries can be handled safely by moving methodically. Stop charging, inspect the equipment, don eyewear, unplug the charger, and detach the clamps last. This process limits the risks until the bloated battery can be properly disposed of and replaced. With care, even battery bubbling can be managed.
Prevention of Battery Bubbling
Lithium-ion battery bloating is often caused by mishandling that leads to gas buildup. However, proper maintenance and charging practices can significantly reduce your risks.
Battery Maintenance
One of the best ways to prevent battery swelling is regular maintenance. As batteries age, their chemistry degrades, making them prone to gassing and bloating.
Replacing older batteries proactively, such as once every 2-3 years, reduces the chances of swelling issues. This ensures you always have a fresh and stable battery inside your device.
Avoid exposing batteries to high temperatures or leaving them fully discharged for long durations. These conditions accelerate swelling triggers like sulfation and electrolyte decomposition.
Periodically inspect device batteries for any signs of early swelling. This allows you to replace an unstable battery before extensive bloating occurs.
Proper Charging
Another key factor is using the correct charging practices and equipment. Always utilize the official OEM charger designed specifically for your device. Universal or off-brand chargers often overcharge.
Keep batteries charging unattended for prolonged periods after reaching total capacity. Stop charging once fully replenished.
Avoid using damaged charging cables that could overload the battery. Regularly inspect lines for wear and tears.
The combination of timely battery replacement, temperature control, discharge avoidance, and proper charging effectively keeps your batteries bubble-free. You can squeeze the safest life from your device batteries with preventative care.
In summary, vigilant maintenance and safe charging habits can minimize swollen battery issues. An ounce of prevention is worth avoiding a pound of bloat!

FAQ
Is it normal for phone batteries to get slightly warm while charging?
Yes, it is normal for your phone battery to get slightly warm during charging cycles. The internal chemical reactions that take place during charging and discharging generate a bit of heat. Under typical usage, this heat is minimal, keeping your battery just slightly above room temperature. But storms that suddenly get hot or heat up when not in use indicate a problem. Always avoid charging damaged, swollen, or leaking phone batteries, as they can overheat dangerously.
My laptop battery is puffing up a little. Is it safe to keep using?
Suppose your laptop battery exhibits mild puffing and swelling but is not leaking, retaining full charge, powering the laptop properly, and not getting hot. In that case, it is safe to use in the short term. However, any swollen battery is degrading and approaching the end of its lifespan. Closely monitor the battery for heat, changing swell size, leakage, or charge issues. Further swelling or new issues arising means it’s time to stop use and replace. For safety, only use the laptop plugged in, so a faulty battery will only leave you stranded once the replacement arrives.
My phone got soaked. Now the battery is swollen. Can I still charge it?
If your phone was immersed in liquid, only attempt to charge it once you get the battery checked out. Fluid can damage phone circuitry to create internal shorts, and trying to set a shorted-soaked battery can cause it to bloat, overheat, or even explode. A swollen, wet battery is hazardous. Do not handle it further, as leaked battery chemicals can burn skin. Please take it to a professional to safely remove and dispose of the battery. Water damage may make your phone unusable even with a new battery, but safety should come first. Do NOT take risks trying to revive a soaked phone.
Can swollen battery issues lead a phone or laptop to explode?
It is rare for swollen lithium-ion batteries in consumer devices like phones and laptops to explode with flames due to gas venting violently. However, the excessive heat and pressure inside a severely ballooned battery can cause it to burst open. This can spray hot leaked chemicals or battery debris, which, while not an explosion, poses a severe risk of burns or eye injury if it happens close to your face. Any phone or laptop battery with severe swelling should be handled cautiously and disposed of properly without delay by taking it to an electronics recycling center. Could you not attempt to puncture or crush it?
My laptop battery got left in the car overnight in below-freezing winter temperatures. Is it safe to use?
A lithium-ion laptop battery exposed to freezing temperatures can suffer performance issues or become damaged. If the battery case has swelled up, the internal material contracts and expands from the cold, causing physical and chemical damage. Do not attempt charging or using a battery suspected to have frozen. Let it gradually warm to room temperature before safely disposing of it. Even if the battery seems to work after freezing, performance problems or premature failure are likely, so it is not recommended to keep using it. Replace the battery and avoid leaving your laptop or its battery in cold temperatures in the future to prevent such damage.
Are there any precautions to take if my phone battery appears to be bubbling or swelling?
If your phone battery exhibits any swelling or bubbling, stop using and charging it immediately and follow these battery safety precautions:
- Avoid handling or disassembling the battery. The chemicals inside can leak and burn skin.
- Do not poke or puncture the storm, which can cause it to spread, smoke, or burst.
- Power the phone down completely and disconnect the battery if possible.
- Protect the phone from flammable objects that could ignite if the battery fails.
- Place the device on a non-flammable surface, like ceramic tile. Do not charge or use on a carpet or bedspread.
- If the phone feels hot, put it on a non-flammable surface outdoors, away from anything flammable, in case of fire.
- Take the device for proper battery disposal and replacement immediately.
- If the battery catches fire, do not attempt to put the fire out. Evacuate the area and call emergency services.
Related Video: hydrogen gas bubbles while charging deep cycle RV batteries (not boiling)
Final Words
In closing, battery bubbling is a sign you should not ignore. While some minor expansion in older batteries is normal, excessive swelling indicates dangerous internal pressure buildup. Stop charging bulging batteries immediately and inspect for leakage, heat, odors, or other red flags. If the battery remains functional but swollen, continue using it cautiously until you can replace it. But dispose of batteries with significant bubbling, odors, heat, or leakage immediately, as they pose risks of fire, burns, and injury. With vigilance and prompt action, you can stay safe and catch battery issues before they escalate. Replace aging batteries to avoid swelling, and you’ll keep your devices charged up without all the drama of bubbles popping up uninvited.